USB Host functions to support Custom Class USB Devices.
More...
|
| | User API |
| | User API reference of the Custom Class.
|
| |
| | Configuration |
| | Configuration of the USB Host Custom Class in µVision.
|
| |
USB Host functions to support Custom Class USB Devices.
The Custom Class in the USB Host Component is used for attaching USB Devices with a specific USB Class to your system. This can either be one of the standard classes that are not directly supported by the USB Middleware or a vendor specific class. Using these functions, you can add support for any USB Device class to the system.
Refer to:
Software Structure
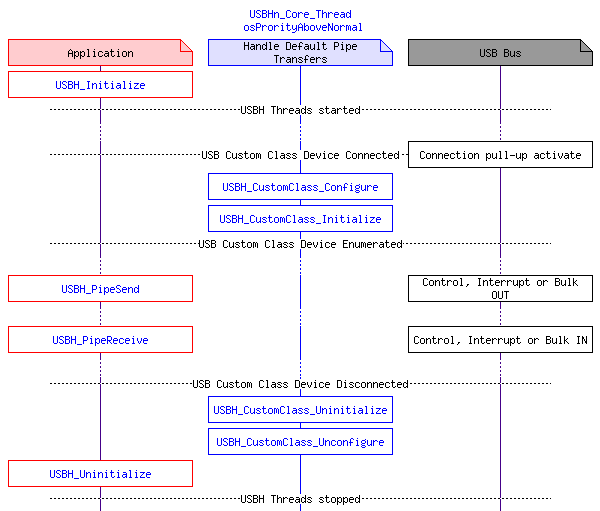
The application starts the USB Host by calling USBH_Initialize. The USB Host Core will wait until an USB Custom Class device is attached to the system. As soon as this happens the Core will configure and initialize the device and it will be ready to be used by the application.
The transmit functions USBH_PipeSend and USBH_PipeReceive will be called by the user thread directly to communicate with the Custom Class device.
As soon as the Custom Class Device is detached from the system, the callback functions USBH_CustomClass_Unconfigure and USBH_CustomClass_Uninitialize signal the removal to the user application.
Implementation
To create an USB Host with support for the Custom class:
User Code Templates
There are two user code templates available that show how to create support for a Custom Class device:
- USBH_User_CustomClass.c shows in general how to use the Custom Class functions.
- USBH_PL2303.c is an actual implementation of the Custom Class functions to add support for Prolific's PL2303 UART to serial RS232 adapter.
User Code Template USBH_User_CustomClass.c
The following source code can be used to implement support for a Custom USB Device Class in the user application.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include "rl_usb.h"
#define CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_CLASS USB_DEVICE_CLASS_VENDOR_SPECIFIC
#define CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_SUBCLASS 0
#define CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_PROTOCOL 0
extern
uint8_t USBH_CC_Device;
uint8_t USBH_CC_Device = 0U;
extern
USB_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR *ptr_if_desc;
USB_ENDPOINT_DESCRIPTOR *ptr_ep_desc;
uint8_t num, i;
(void)ptr_dev_desc;
USBH_CC_Device = device;
for (i = 0U; i < 8U; i++) {
USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i] = 0U;
}
ptr_if_desc = (USB_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR *)((uint32_t)ptr_cfg_desc + ptr_cfg_desc->
bLength);
num = ptr_if_desc->bNumEndpoints;
switch (ptr_if_desc->bInterfaceClass) {
case CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_CLASS:
switch (ptr_if_desc->bInterfaceSubClass) {
case CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_SUBCLASS:
switch (ptr_if_desc->bInterfaceProtocol) {
case CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_PROTOCOL:
ptr_ep_desc = (USB_ENDPOINT_DESCRIPTOR *)((uint32_t)ptr_if_desc + ptr_if_desc->bLength);
i = 0U;
while (num-- != 0U) {
pipe_hndl =
USBH_PipeCreate (device, ptr_ep_desc->bEndpointAddress, ptr_ep_desc->bmAttributes & USB_ENDPOINT_TYPE_MASK, ptr_ep_desc->wMaxPacketSize & 0x7FFU, ptr_ep_desc->bInterval);
if (pipe_hndl == 0U) {
for (i = 0U; i < 8U; i++) {
if (USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i] != 0U) {
USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i] = 0U;
}
}
return 255U;
}
USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i++] = pipe_hndl;
ptr_ep_desc++;
}
return 0U;
default:
break;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
return 255U;
}
uint8_t i;
(void)instance;
USBH_CC_Device = 0U;
for (i = 0U; i < 8U; i++) {
if (USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i] != 0U) {
USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i] = 0U;
}
}
}
(void)instance;
}
(void)instance;
}
User Code Template USBH_PL2303.c
The following source code implements support for Prolific's PL2303 UART to serial RS232 adapter using the Custom Class functions.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include "rl_usb.h"
#define CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_CLASS USB_DEVICE_CLASS_VENDOR_SPECIFIC
#define CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_SUBCLASS 0
#define CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_PROTOCOL 0
extern
uint8_t USBH_CC_Device;
uint8_t USBH_CC_Device = 0U;
extern
USB_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR *ptr_if_desc;
USB_ENDPOINT_DESCRIPTOR *ptr_ep_desc;
uint8_t num, i;
USBH_CC_Device = device;
for (i = 0U; i < 8U; i++) {
USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i] = 0U;
}
ptr_if_desc = (USB_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR *)((uint32_t)ptr_cfg_desc + ptr_cfg_desc->
bLength);
num = ptr_if_desc->bNumEndpoints;
return 255U;
}
switch (ptr_if_desc->bInterfaceClass) {
case CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_CLASS:
switch (ptr_if_desc->bInterfaceSubClass) {
case CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_SUBCLASS:
switch (ptr_if_desc->bInterfaceProtocol) {
case CUSTOM_CLASS_IF_PROTOCOL:
ptr_ep_desc = (USB_ENDPOINT_DESCRIPTOR *)((uint32_t)ptr_if_desc + ptr_if_desc->bLength);
i = 0U;
while (num-- != 0U) {
pipe_hndl =
USBH_PipeCreate (device, ptr_ep_desc->bEndpointAddress, ptr_ep_desc->bmAttributes & USB_ENDPOINT_TYPE_MASK, ptr_ep_desc->wMaxPacketSize & 0x7FFU, ptr_ep_desc->bInterval);
if (pipe_hndl == 0U) {
for (i = 0U; i < 8U; i++) {
if (USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i] != 0U) {
USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i] = 0U;
}
}
return 255U;
}
USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i++] = pipe_hndl;
ptr_ep_desc++;
}
return 0U;
default:
break;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
return 255U;
}
uint8_t i;
(void)instance;
USBH_CC_Device = 0U;
for (i = 0U; i < 8U; i++) {
if (USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i] != 0U) {
USBH_CC_PipeHandle[i] = 0U;
}
}
}
uint32_t br;
uint8_t buf[8];
(void)instance;
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(0x8484U);
setup_packet.
wIndex = U16_LE(0U);
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(0x0404U);
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(0x8484U);
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(0x8383U);
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(0x8484U);
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(0x0404U);
setup_packet.
wIndex = U16_LE(1U);
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(0x8484U);
setup_packet.
wIndex = U16_LE(0U);
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(0x8383U);
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(0U);
setup_packet.
wIndex = U16_LE(1U);
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(1U);
setup_packet.
wIndex = U16_LE(0U);
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(2U);
setup_packet.
wIndex = U16_LE(0x44U);
setup_packet.
wValue = U16_LE(0U);
setup_packet.
wIndex = U16_LE(0U);
br = U32_LE(9600U);
buf[0] = (uint8_t)( br & 0xFFU);
buf[1] = (uint8_t)((br >> 8) & 0xFFU);
buf[2] = (uint8_t)((br >> 16) & 0xFFU);
buf[3] = (uint8_t)((br >> 24) & 0xFFU);
buf[4] = 0U;
buf[5] = 0U;
buf[6] = 8U;
}
(void)instance;
}