|
||
| Products Download Events Support Videos | ||
Technical Support
On-Line Manuals
µVision3 User's Guide


 Breakpoints
Breakpoints
![]() µVision3 lets you define breakpoints in several
different ways. You may already set Execution Breaks during
editing of your source text, even before the program code is
translated. Breakpoints can be defined and modified in the following
ways:
µVision3 lets you define breakpoints in several
different ways. You may already set Execution Breaks during
editing of your source text, even before the program code is
translated. Breakpoints can be defined and modified in the following
ways:
- With the File Toolbar buttons. Just select the code line in the Editor or Disassembly window and click on the breakpoint buttons.
- With the breakpoint commands in the local menu. The local menu opens with a right mouse click on the code line in the Editor or Disassembly window.
- The Debug — Breakpoints… dialog lets you review, define and modify breakpoint settings. This dialog allows you to define also access breakpoints with different attributes. Refer to the examples below.
- In the Output Window — Command page you can use the BreakSet, BreakKill, BreakList, BreakEnable, and BreakDisable commands.
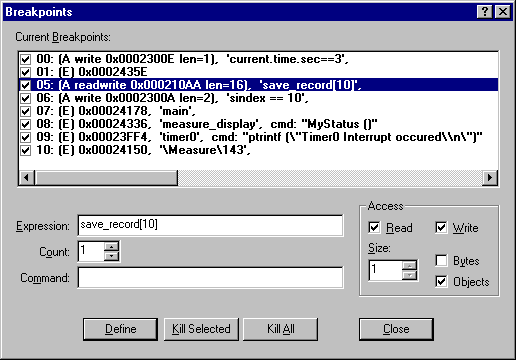
The Breakpoint dialog lets you view and modify breakpoints. You can quickly disable or enable the breakpoints with a mouse click on the check box in the Current Breakpoints list. A double click in the Current Breakpoints list allows you to modify the selected break definition.
You define a breakpoint by entering an Expression in the Breakpoint dialog. Depending on the expression one of the following breakpoint types is defined:
- When the expression is a code address, an Execution Break (E) is defined that becomes active when the specified code address is reached. The code address must refer to the first byte of a CPU instruction.
- When a memory Access (Read, Write or both) is selected an Access Break (A) is defined that becomes active when the specified memory access occurs. You can specify the size of the memory access window in bytes or object size of the expression. Expressions for an Access Break must reduce to a memory address and memory type. The operators (&, &&, <. <=. >, >=, = =, and !=) can be used to compare the variable values before the Access Break halts program execution or executes the Command.
- When the expression cannot be reduced to an address a Conditional Break (C) is defined that becomes active when the specified conditional expression becomes true. The conditional expression is recalculated after each CPU instruction, therefore the program execution speed may slow down considerably.
When you specify a Command for a breakpoint, µVision3 executes the command and resumes executing your target program. The command you specify here may be a µVision3 debug or signal function. To halt program execution in a µVision3 function, set the _break_ system variable. For more information refer to System Variables.
The Count value specifies the number of times the breakpoint expression is true before the breakpoint is triggered.
Breakpoint Examples:
The following description explains the definitions in the Breakpoint dialog shown above. The Current Breakpoints list summarizes the breakpoint type and the physical address along with the Expression, Command and Count.
| Expression: | \Measure\143 | Execution Break (E) that halts when the target program reaches the code line 143 in the module MEASURE. |
| Expression: | main | Execution Break (E) that halts when the target program reaches the main function. |
| Expression: Command: |
timer0 printf ("T0 Interrupt Occurred") |
Execution Break (E) that prints T0 Interrupt occurred in the Output Window – Command page when the target program reaches the timer0 function. |
| Expression: Count: |
save_measurements 10 |
Execution Break (E) that halts when the target program reaches the function save_measurements the 10th time. |
| Expression: |
mcommand == 1 | Conditional Break (C) that halts program execution when the expression mcommand == 1 becomes true. This breakpoint is disable in the above Breakpoint dialog. |
| Expression: Access: Size: |
save_record[10] Read Write 3 Objects |
Access Break (A) that halts program execution when an read or write access occurs to save_record[10] and the following 2 objects. Since save_record is a structure with size 16 bytes this break defines an access region of 48 bytes. |
| Expression: Access: |
sindex == 10 Write |
Access Break (A) that halts program execution when the value 10 is written to the variable sindex. |
| Expression: Command: |
measure_display MyStatus () |
Execution Break (E) that executes the uVision debug function MyStatus when the target program reaches the function measure_display. The target program execution resumes after the debug function MyStatus has been executed. |
ProductsDevelopment Tools |
Hardware & Collateral |
Downloads |
Support |
Contact |
